Feature Engine
Discovery
Declare owners and metadata for features.
Features can capture metadata to inform
alerting, monitoring, and discovery.
By default, features are created as any type-annotated
variable of a class decorated with @features.
However, you may also assign these variables to the
result of the chalk.features.feature(...) function
to provide metadata.
Description
Descriptions are parsed from the comments preceding
the feature definition. For example, you can document a
fraud_score feature with information about the values
as follows:
@features
class User:
# 0 to 100 score indicating an identity match.
# Low scores indicate safer users
fraud_score: float
...You can alternatively provide a description of a feature directly in the code. The following example is equivalent to explicitly providing the description as above:
@features
class User:
fraud_score: float = feature(description="""
0 to 100 score indicating an identity match.
Low scores indicate safer users
""")
...If both an explicit description and a comment are present,
the description will be set to the explicit value from
feature(description=...).
You can programmatically access the description for a feature
with the description(...) function:
from chalk.feature import description
print(description(User.fraud_score))Owner
You may also specify which person or group is responsible for an individual feature. The owner tag will be available in Chalk’s web portal. Alerts that do not otherwise have an owner will be assigned to the owner of the monitored feature. Owners are parsed from the source code. For example:
@features
class User:
full_name: str
# :owner: katherine.johnson@nasa.gov
fraud_score: float
...You may instead choose to specify an owner via a keyword argument to
feature().
For example:
@features
class User:
full_name: str
fraud_score: float = feature(owner="katherine.johnson@nasa.gov")
...An owner can also be assigned to every feature in a namespace via a keyword argument to @features:
@features(owner="katherine.johnson@nasa.gov")
class User:
full_name: str
fraud_score: float
# :owner: annie.easley@nasa.gov
email: str
...Here, User.full_name and User.fraud_score
assume the owner katherine.johnson@nasa.gov.
However, User.email, which specifies an owner at the feature level,
assumes the owner annie.easley@nasa.gov.
You can programmatically access the owner of a feature
with the owner(...) function:
from chalk.feature import owner
assert owner(User.email) == "annie.easley@nasa.gov"Tags
Tags are a way of adding metadata to features for use in filtering, aggregations, and visualizations. For example, you can use tags to assign features to a team and find all features for a given team.
@features
class User:
# :tags: team:identity, priority:high
fraud_score: float
...Alternatively, you may specify tags via explicit construction:
@features
class User:
fraud_score: float = feature(tags=[
"team:identity",
"priority:high",
])
...As with the owner property, tags can be assigned to all features in a namespace:
@features(tags="group:risk")
class User:
fraud_score: float
# :tags: pii
email: str
...Here, User.fraud_score inherits the tag group:risk.
The feature User.email will also inherit this tag
in addition to the tag pii.
You can programmatically access the tags for a feature
with the tags(...) function:
from chalk.feature import tags
assert tags(User.email) == ["pii", "group:risk"]Semantic search
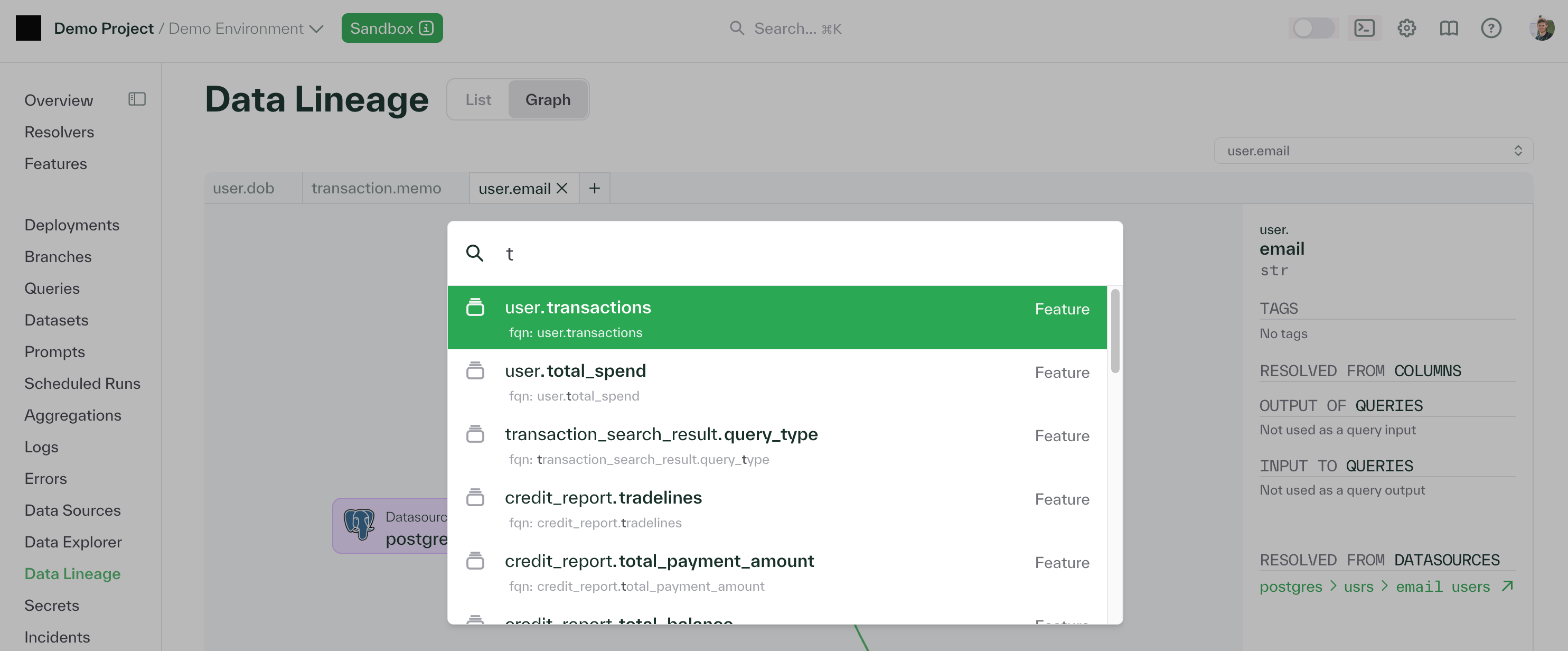
Chalk provides powerful semantic search capabilities to help you quickly find features across your entire feature catalog. You can access semantic search in two ways:
- Keyboard shortcut: Press
Cmd+K(Mac) orCtrl+K(Windows/Linux) from anywhere in the Chalk web interface - Search button: Click the search icon in the header navigation bar
The semantic search understands natural language queries and searches across:
- Feature names and namespaces
- Feature descriptions and documentation
- Owner information
- Tags and metadata
- Resolver implementations
This makes it easy to find features even when you don’t know their exact names. For example, you can search for “user risk features” or “features updated last week” or “features owned by data team”.
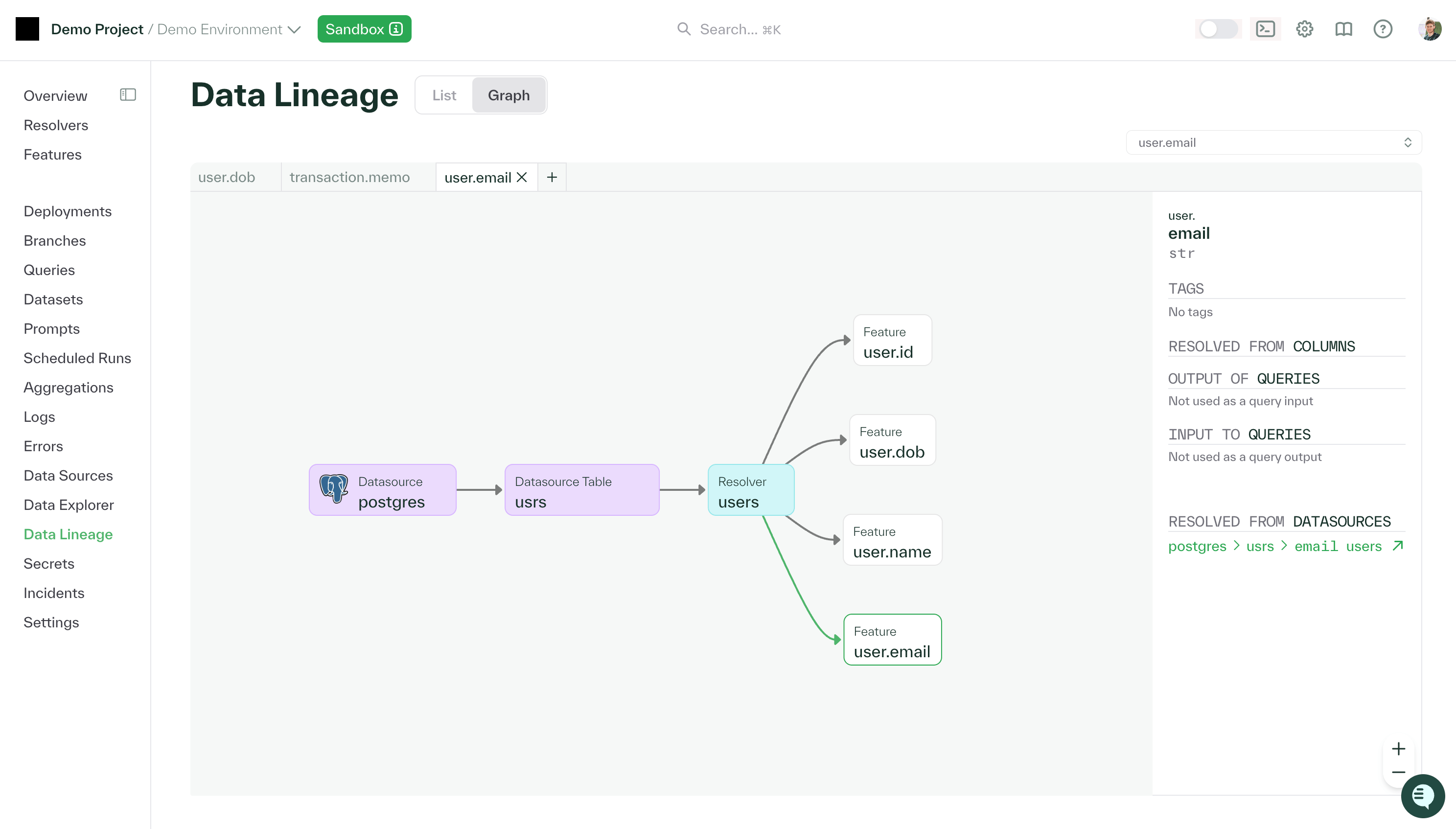
Data lineage
Understanding how features are computed and what data they depend on is critical for debugging, compliance, and impact analysis. Chalk automatically tracks and visualizes the complete data lineage for every feature.
The data lineage view shows:
- Upstream dependencies: Data sources, SQL queries, and other features that this feature depends on
- Downstream consumers: Features, models, and queries that depend on this feature
- Resolver chain: The sequence of resolvers that compute this feature
- Data sources: External databases, APIs, and streaming sources that provide raw data
You can access the lineage view by clicking on any feature in the web interface and selecting the “Lineage” tab. The interactive graph allows you to explore dependencies, trace data flow, and understand the full context of how a feature is computed.
This visualization is particularly useful for:
- Impact analysis: Before modifying a feature, see what downstream features and models would be affected
- Debugging: Trace back through the computation graph to identify where issues may be occurring
- Compliance: Document data provenance for regulatory requirements
- Optimization: Identify redundant computations or opportunities to consolidate resolvers